LeetCode
2130. Maximum Twin Sum of a Linked List
10002s
2023. 11. 19. 00:44
Maximum Twin Sum of a Linked List - LeetCode
크기가 n인 링크드 리스트가 주어집니다. 여기서 n은 짝수이며, 링크드 리스트의 i번째 노드(0부터 인덱싱)는 (n-1-i)번째 노드의 쌍으로 알려져 있습니다. 즉, 0 <= i <= (n / 2) - 1인 경우 i번째 노드는 (n-1-i)번째 노드의 쌍이라고 합니다.
예를 들어, n = 4이면 노드 0은 노드 3의 쌍이며, 노드 1은 노드 2의 쌍입니다. 이들은 n = 4인 경우에만 있는 쌍 중 유일한 노드들입니다. 쌍의 합은 노드와 해당 노드의 쌍의 합으로 정의됩니다.
주어진 짝수 길이의 링크드 리스트의 최대 쌍 합을 반환하세요.
In a linked list of size n, where n is even, the ith node (0-indexed) of the linked list is known as the twin of the (n-1-i)th node, if 0 <= i <= (n / 2) - 1.
- For example, if n = 4, then node 0 is the twin of node 3, and node 1 is the twin of node 2. These are the only nodes with twins for n = 4.
The twin sum is defined as the sum of a node and its twin.
Given the head of a linked list with even length, return the maximum twin sum of the linked list.
Example 1:

Input: head = [5,4,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes 0 and 1 are the twins of nodes 3 and 2, respectively. All have twin sum = 6.
There are no other nodes with twins in the linked list.
Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is 6.
Example 2:
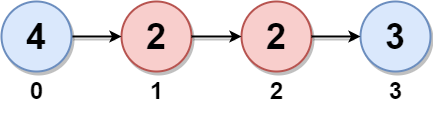
Input: head = [4,2,2,3]
Output: 7
Explanation:
The nodes with twins present in this linked list are:
- Node 0 is the twin of node 3 having a twin sum of 4 + 3 = 7.
- Node 1 is the twin of node 2 having a twin sum of 2 + 2 = 4.
Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is max(7, 4) = 7.
Example 3:

Input: head = [1,100000]
Output: 100001
Explanation:
There is only one node with a twin in the linked list having twin sum of 1 + 100000 = 100001.
풀이과정 설명:
- 링크드 리스트를 반으로 나누어 왼쪽과 오른쪽 부분으로 나눕니다.
- 나뉜 두 부분을 역순으로 뒤집습니다.
- 두 부분을 순회하면서 각 노드와 해당 노드의 쌍의 합을 구하고, 최대 쌍 합을 갱신합니다.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pairSum(ListNode head) {
int listSize = getListSize(head);
ListNode leftNode = head;
ListNode rightNode = getBackList(head, listSize);
rightNode = getReverseList(rightNode);
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= listSize /2 - 1; i++){
int sum = leftNode.val + rightNode.val;
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, sum);
leftNode = leftNode.next;
rightNode = rightNode.next;
}
return maxSum;
}
public int getListSize(ListNode head){
int count = 0;
while(head != null){
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
public ListNode getBackList(ListNode head, int listSize){
for(int i = 0; i < listSize/2 - 1; i++){
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
public ListNode getReverseList(ListNode head){
ListNode beforeNode = null;
while(head != null){
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
head.next = beforeNode;
beforeNode = head;
head = nextNode;
}
return beforeNode;
}
}굳이 이렇게 어렵게 구해야하는가?
아래식이 훨 편하구만~
풀이과정 설명:
- 링크드 리스트를 ArrayList 로 저장한다.
- ArrayList 를 앞에서 부터 차곡차곡 + 뒤에서 부터 차곡차곡 더하면서 최대값을 갱신한다.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pairSum(ListNode head) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
while(head != null){
arrList.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int arrLength = arrList.size();
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arrLength /2; i++){
int sum = arrList.get(i) + arrList.get(arrLength - 1 - i);
maxSum = Math.max(sum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
}반응형