고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
LeetCode - The World's Leading Online Programming Learning Platform
연결 리스트의 헤드(첫 노드)가 주어집니다. 중간 노드를 삭제하고 수정된 연결 리스트의 헤드를 반환하세요.
크기가 n인 연결 리스트의 중간 노드는 0부터 시작하는 인덱싱에서 ⌊n / 2⌋ 번째 노드입니다. 여기서 ⌊x⌋는 x 이하의 가장 큰 정수를 나타냅니다.
예를 들어, n이 1, 2, 3, 4, 5일 때 중간 노드는 각각 0, 1, 1, 2, 2입니다.
You are given the head of a linked list. Delete the middle node, and return the head of the modified linked list.
The middle node of a linked list of size n is the ⌊n / 2⌋th node from the start using 0-based indexing, where ⌊x⌋ denotes the largest integer less than or equal to x.
- For n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, the middle nodes are 0, 1, 1, 2, and 2, respectively.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,3,4,7,1,2,6]
Output: [1,3,4,1,2,6]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list. The indices of the nodes are written below.
Since n = 7, node 3 with value 7 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
We return the new list after removing this node.
Example 2:
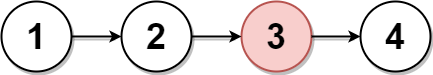
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,4]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 4, node 2 with value 3 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
Example 3:

Input: head = [2,1]
Output: [2]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 2, node 1 with value 1 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
Node 0 with value 2 is the only node remaining after removing node 1.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 105].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
풀이과정:
중간 노드 찾기:
연결 리스트를 두 번 순회하지 않고 중간 노드를 찾기 위해 두 개의 포인터를 사용합니다. 하나는 노드를 한 번에 하나씩 이동하는 slow 포인터이고, 다른 하나는 fast 포인터로 한 번에 두 개의 노드씩 이동합니다.
fast 포인터가 연결 리스트의 끝에 도달하면, slow 포인터는 중간 노드에 도달합니다.
중간 노드 삭제:
중간 노드를 삭제하려면 해당 노드의 이전 노드를 알아야 합니다. prev 포인터를 사용하여 중간 노드의 이전 노드를 찾습니다.
prev 포인터의 next를 중간 노드의 next로 설정하여 중간 노드를 건너 뛰게 만듭니다.
결과 반환:
중간 노드를 삭제한 후, 수정된 연결 리스트의 헤드를 반환합니다.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteMiddle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode node1 = head;
ListNode node2 = head;
ListNode bNode = null;
while (node2 != null && node2.next != null) {
bNode = node1;
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next.next;
}
bNode.next = node1.next;
return head;
}
}
반응형
'LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 1448. Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree (0) | 2023.10.26 |
|---|---|
| 872. Leaf-Similar Trees (0) | 2023.10.26 |
| 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (0) | 2023.10.26 |
| 394. Decode String (0) | 2023.10.26 |
| 2352. Equal Row and Column Pairs (0) | 2023.10.26 |




